Cyber Threats

Introduction to Cyber Threats
In the vast expanse of cyberspace, where information flows ceaselessly and digital interactions weave the fabric of our connected world, the specter of cyber threats looms ominously. Cybersecurity has become an indispensable shield against the myriad dangers that inhabit the digital landscape. This article takes a deep dive into the realm of cyber threats, exploring the different forms they take, the risks they pose, and how individuals and organizations can fortify their defenses against these digital menaces.
Malware
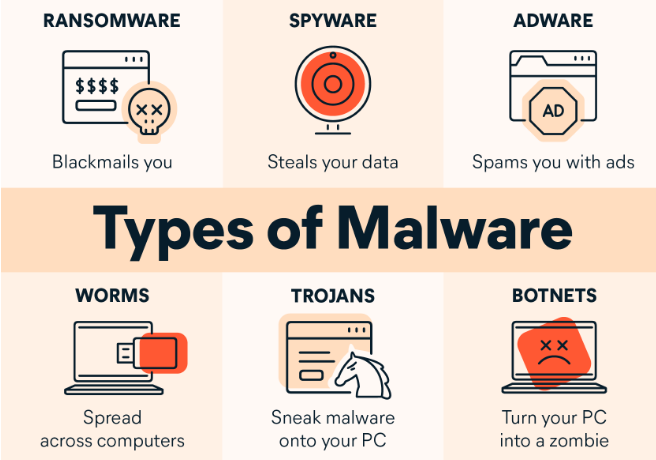
Understanding Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a broad category of software designed to harm or exploit devices, networks, and data. It includes viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware, each with its own nefarious purpose.
Example: WannaCry Ransomware Attack
The WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 infected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide. It encrypted users’ files and demanded a ransom in Bitcoin for their release. This incident highlighted the destructive potential of malware on a global scale.
Resource: Types of Malware and How to Defend Against Them
Phishing
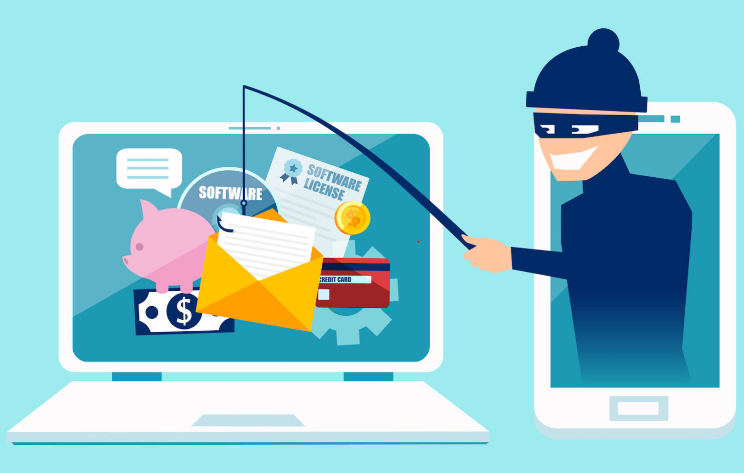

Deconstructing Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a deceptive technique where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details. Phishing attacks often arrive via email, enticing users to click on malicious links or provide confidential data.
Example: Email Spoofing
In an email spoofing attack, cybercriminals forge the sender’s address to appear trustworthy, increasing the likelihood of users falling for phishing scams. Spoofed emails often mimic official communication from banks, government agencies, or reputable organizations.
Resource: How to Recognize and Avoid Phishing Scams
MITM Attack
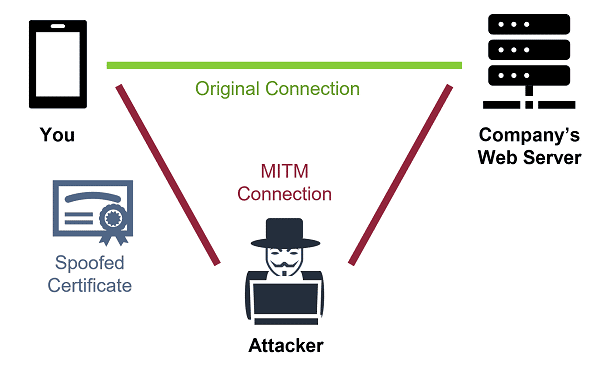
Unmasking Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
A Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack occurs when an unauthorized entity intercepts and potentially alters communication between two parties. This can lead to the theft of sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial data.
Example: Wi-Fi Eavesdropping
In a Wi-Fi eavesdropping attack, an attacker positions themselves between a user and a Wi-Fi network, intercepting and monitoring the data exchanged. This allows the hacker to capture sensitive information transmitted over the network.
Resource: Man-in-the-Middle Attacks Explained
DDOS Attack
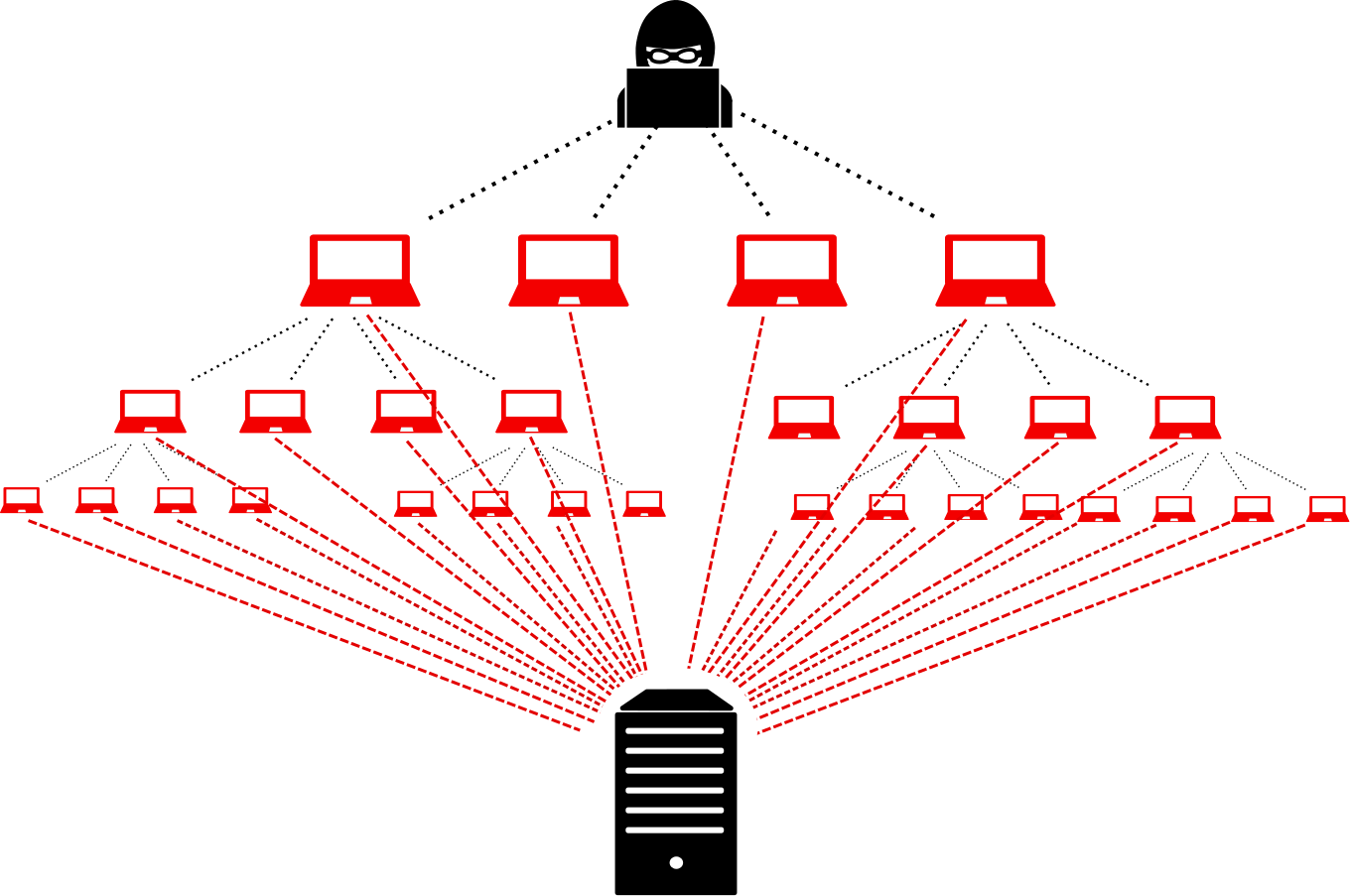
Unraveling Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks involve flooding a network, service, or website with an overwhelming volume of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to users. This is achieved by coordinating the efforts of multiple compromised devices.
Example: Mirai Botnet Attack
The Mirai botnet, composed of infected Internet of Things (IoT) devices, launched massive DDoS attacks in 2016. The targeted websites experienced severe disruptions, highlighting the vulnerability of interconnected devices.
Resource: How to Protect Against DDoS Attacks
Password Attack
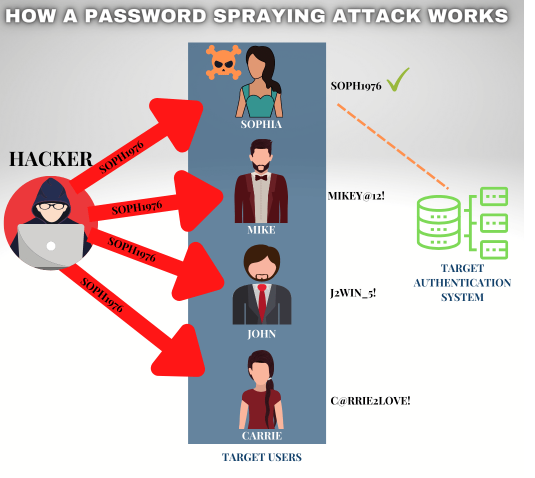
Cracking the Code on Password Attacks
Password attacks involve unauthorized attempts to access an individual’s or organization’s accounts by exploiting weak or compromised passwords. Attackers use various techniques, including brute force attacks, credential stuffing, and dictionary attacks.
Example: Brute Force Attack
In a brute force attack, hackers systematically try all possible combinations of passwords until they find the correct one. This method is time-consuming but can be successful against weak or easily guessable passwords.
Resource: Common Password Attacks and How to Defend Against Them
Malvertising Attack
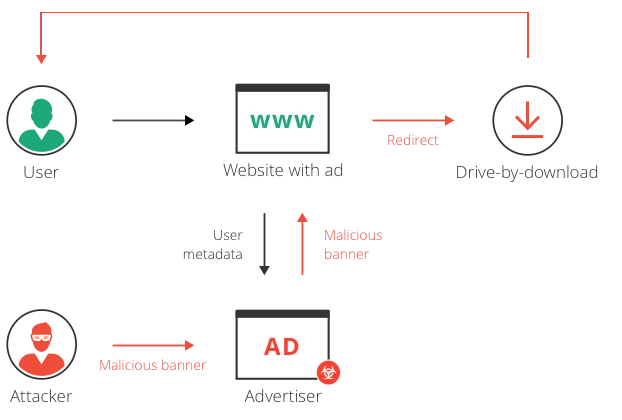
Demystifying Malvertising
Malvertising, a portmanteau of “malicious” and “advertising,” involves injecting malicious code into online advertisements. Users unwittingly encounter these ads on legitimate websites, leading to the inadvertent download of malware.
Example: The Kyle and Stan Malvertising Campaign
The Kyle and Stan malvertising campaign targeted popular websites, delivering malware to users through infected online ads. This tactic exploited the trust users place in reputable websites, demonstrating the insidious nature of malvertising.
Resource: What is Malvertising and How to Protect Against It
Rogue Software
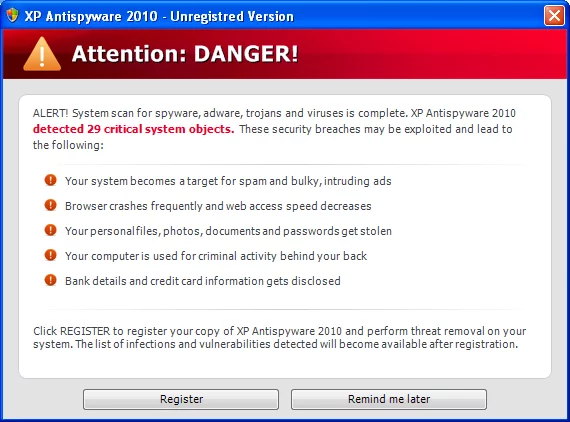
Identifying Rogue Software Threats
Rogue software, also known as scareware or fake antivirus software, deceives users into downloading and installing malicious programs under the guise of legitimate security tools. These programs often generate false security alerts, urging users to pay for unnecessary services.
Example: FakeAV Scams
Fake antivirus scams trick users into installing counterfeit security software. Once installed, the rogue software may display alarming messages about nonexistent threats, pressuring users to purchase fraudulent security solutions.
Resource: How to Avoid Fake Antivirus Scams

Safeguarding Against Cyber Threats
1. Stay Informed and Educated
Knowledge is the first line of defense. Stay informed about the latest cyber threats, tactics, and best practices. Regularly educate yourself and your team on cybersecurity awareness.
Resource: Cyber Security Awareness Training Programs
2. Implement Robust Security Measures
Deploy comprehensive security measures, including firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and encryption. Regularly update and patch systems to address vulnerabilities promptly.
Resource: Best Practices for Cyber Security
3. Use Strong and Unique Passwords
Encourage the use of strong, unique passwords for each account. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible to add an extra layer of security.
Resource: Creating Strong Passwords and Tips for Keeping Them Safe
4. Be Wary of Unsolicited Emails and Ads
Exercise caution when encountering unsolicited emails, especially those requesting personal information. Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
5. Regularly Backup Important Data
Regularly back up critical data to prevent data loss in the event of a cyber attack. Ensure that backups are stored securely and can be easily restored.
Resource: Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) – Data Backup Resources
Concluding Thoughts
In the complex dance between cyber threats and defenders, vigilance, education, and proactive measures are our greatest allies. The landscape of cyber threats is ever-changing, requiring a dynamic and adaptive approach to cybersecurity.
As we navigate the digital frontier, let us fortify our defenses, share knowledge, and foster a culture of cyber resilience. By staying informed and implementing robust cybersecurity practices, we can collectively mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats, ensuring a safer and more secure digital future.
In conclusion, the battle against cyber threats is ongoing, but with knowledge, preparation, and a collaborative spirit, we can stand resilient against the digital menace. As technology continues to advance, let us evolve our defenses to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s cyber landscape. Together, we can create a digital world where security and connectivity coexist harmoniously.
Also read this(recommended)





I enjoy your website, obviously, but you should check the spelling on a number of your posts. A number of them have numerous spelling errors, which makes it difficult for me to tell the truth, but I will definitely return.
thanks for this information i will work on it .